
Universal File Analyzer
Product Help File
Universal File Analyzer (UFA) revolutionizes your file management experience with its File Analyzer function. This powerful tool is designed to identify file types with precision by analyzing file signatures. By scanning the content of files, the File Analyzer determines the most suitable file extension type, making it the standout feature of UFA.
But UFA doesn’t stop there. Beyond its File Analyzer capabilities, it retains an extensive multi-format file viewer that supports over 400 file formats. This comprehensive viewer allows you to seamlessly open and interact with various file types, eliminating the need for multiple specialized viewers. Whether you’re a professional managing diverse file formats or an everyday user seeking an efficient and user-friendly file management solution, UFA is your trusted companion for effortless file management and viewing.
– Sponsored Links –
This product help file is designed to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the application, so you can make the most of its features and functions. The following topics will be covered to ensure that you have a thorough understanding of the application and how to use it effectively.
Open Universal File Analyzer
To launch Universal File Analyzer (UFA) after installation, follow these simple steps:
- Click the Windows Start button.
- In the search bar, type “Universal File Analyzer“
- Look for the application with the matching name and this app icon
 .
. - Click the application entry to launch UFA.
By following these steps, you can quickly and easily launch UFA and start using its powerful file viewing capabilities.
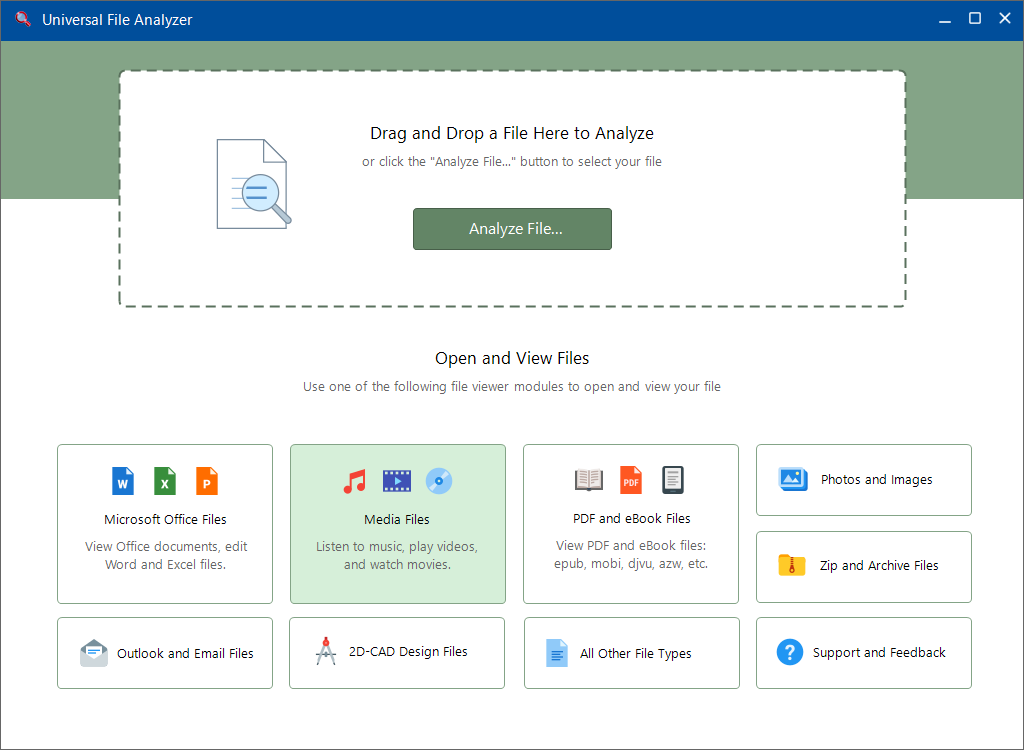
Quick Start – How to Analyze a File
One of the primary features of UFA is its ability to detect file type extensions by analyzing file content. UFA scans for digital signatures that are identical or similar to file types known to the application, providing precise identification of file types. You can initiate the file analysis process in two simple ways:
1. Drag-n-Drop: Begin by selecting the file you want to analyze from Windows Explorer, then drag it into the designated “Drag-n-Drop” zone located in the Main window. For more details on using the Drag-n-Drop feature, refer to the “File Analyzer Control” section below.
2. Click the “Analyze File…” Button: Alternatively, click the “Analyze File…” button to open the file dialog. Locate the target file using the dialog, and once you’ve selected it, click the “OK” button.
By employing either of these methods, you can swiftly initiate the file analysis process, allowing UFA to identify the file type by scanning its content. Once the analysis is complete, the app presents the results in the File Analyzer Report window.
– Sponsored Links –
File Analyzer Report
The File Analyzer Report window presents the scan results, including the identified file extension type and file attributes.
If the file type is supported by UFA’s embedded file viewer, you can also open and view the file by clicking the “Open File” button.
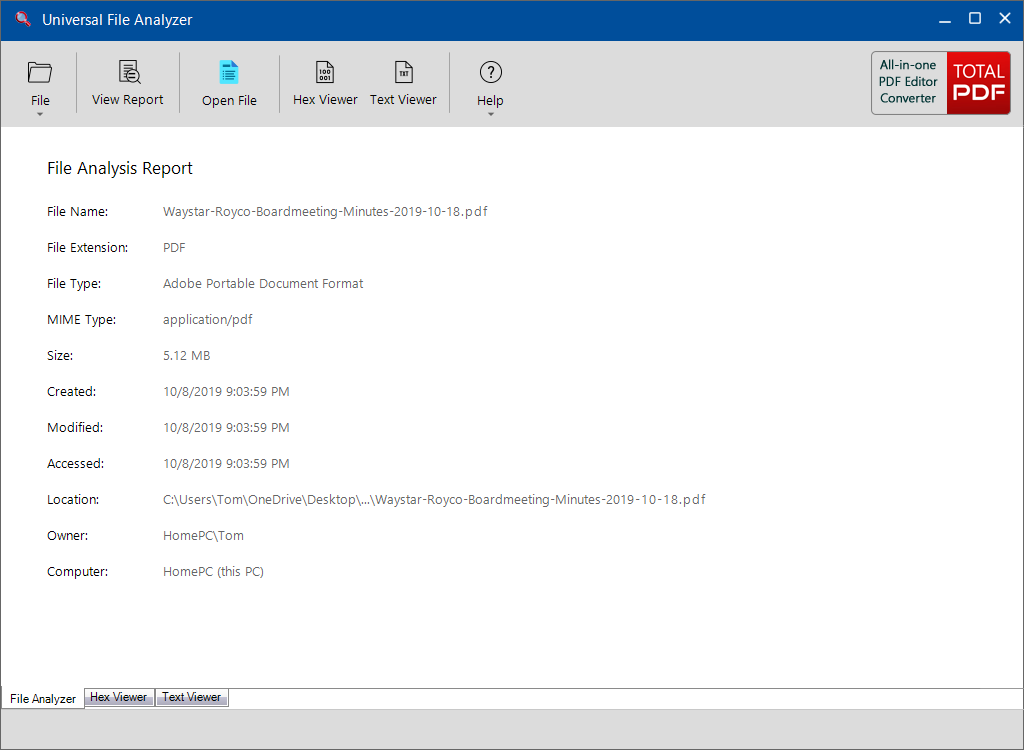
File type extension information
File Extension: This field displays the specific file extension associated with the analyzed file. For example, a PDF file would have the file extension “.PDF.”
File Type: In this field, you’ll find the descriptive name of the file format. For instance, a PDF file is identified as “Adobe Portable Document Format,” which provides information about the file’s format and purpose.
MIME Type: The MIME Type field indicates the Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) type associated with the file. For a PDF file, the MIME Type is typically “application/PDF.” This information is important for web browsers and other applications to understand how to handle the file.
Windows file attributes
File Size: This attribute indicates the size of the file in bytes or a more human-readable format, such as kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), or gigabytes (GB). It tells you how much storage space the file occupies on your storage device.
Created Time: The Created Time attribute displays the date and time when the file was initially created or added to the storage location. It provides information about when the file was first introduced into the system.
Modified Time: This attribute shows the date and time when the file was last modified or altered. It is updated whenever changes are made to the file’s content, properties, or attributes.
Accessed Time: The Accessed Time attribute indicates the date and time when the file was last accessed or opened. This timestamp reflects the most recent time the file was viewed or interacted with.
Location: Location specifies the directory or folder where the file is stored within the file system’s hierarchy. It provides the file’s path, helping users navigate to its exact location.
Owner: The Owner attribute displays the username or account associated with the file’s ownership. It identifies the individual or entity responsible for the file.
Computer: The Computer attribute specifies the name of the computer or device where the file is currently located. This information is particularly useful in networked environments where files may be stored on various computers or servers.
– Sponsored Links –
– Sponsored Links –
How to Open a File
For those who are eager to get started, there are several ways to open a file using the Universal File Viewer:
Use one of the File Viewer Modules located on the main window. If you know the type of file you want to open, select a module that matches the file type, otherwise, simply choose “All other file types” to open the file.
Right-Click: You can right-click on a file in Windows Explorer and select “Open with > Universal File Analyzer“.
The Viewer Module: You can click on one of the viewer module tiles in the Main window to launch the Open File dialog box and select the file you want to open. Learn more about the Viewer Modules.
File Menu: Within the File Analysis Report window or any individual viewer module window, you can use the “File > Open” menu to select the file you want to open.
Recently Opened Files List: If the file you want to open is in the list of recently opened files, you can access it directly from the Recently Opened Files list from the File menu in the File Analysis Report window, as well as from each viewer module. Learn more about the Recently Opened File List.
By using any of these methods, you can easily open and view your files in Universal File Analyzer.
The Main Window
The Universal File Analyzer’s main window serves as the central hub, providing easy access to the application’s various functions and features. It is designed with user-friendliness in mind and consists of three main areas to streamline your file viewing experience:
File Analyzer Control: offers access to the File Analyzer function.
Viewer Modules: offers entry points to all file viewer modules.
Recently Opened File: keeps a list of recently opened files for easy access.
Please keep in mind that closing the main window of the Universal File Analyzer will exit the application entirely. To continue using the app, you can minimize the application to the system tray or use other operating system-specific methods for keeping the app running in the background.
– Sponsored Links –
File Analyzer Control
The File Analyzer Control, situated at the top of the main window, offers a user-friendly and efficient way to perform file type analysis.
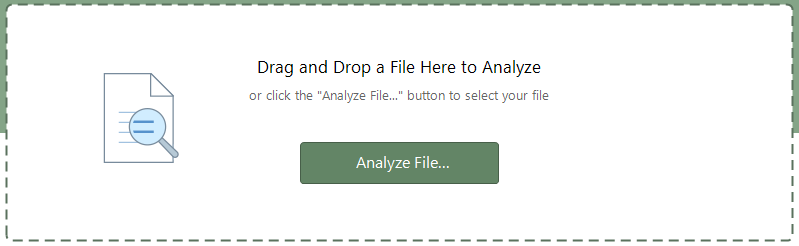
You can perform file type analysis using one of two methods. First, click the “Analyze File…” button to open the system’s file browser dialog, allowing easy navigation through your computer’s directories. Locate the file you would like to analyze and then click the OK button.
Alternatively, the drag-and-drop method simplifies file access, letting you seamlessly open files supported by the Universal File Analyzer with just a quick drag and drop action:
- Open Windows Explorer: Navigate to the location of the file you want to analyze using Windows Explorer (File Explorer).
- Drag and Drop: Click and drag the desired file from Windows Explorer and drop it into the Universal File Analyzer’s drop-n-drop zone in the main window.
The Universal File Analyzer will scan the selected file and displays the scan result in the File Analysis Report window.
– Sponsored Links –
The Viewer Modules
Universal File Analyzer is built with a flexible and expandable architecture, combining a group of viewer modules. Each module provides viewing (and sometimes even editing) functionality for a set of file types, including audio, video, images, and more.
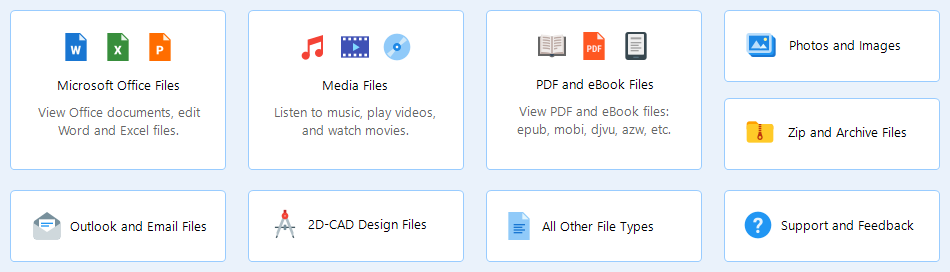
There are 10 viewer modules in the latest version of UFA:
- Microsoft Office files: View and edit Office documents, including Word and Excel files.
- Media files: Listen to music, play videos, and watch movies effortlessly.
- PDF and eBooks files: Open and view PDF and eBook files, including popular formats like ePub, Mobi, djvu, azw, and more.
- Photos and images: View and print various image formats, such as PNG, BMP, JPEG, Tiff, Gif, and more.
- Zip and archive files: Supports opening a wide range of archived zip files, including 7z, zip, gzip, tgz, and more.
- Outlook and email files: View email files saved in EML and MSG formats, making it easy to access and read your email content.
- 2D CAD files: Facilitates the viewing of 2-dimensional CAD designs in formats like DWG and DXF, ensuring easy access to technical drawings.
- Text files: Open and view text-based documents and files with ease using this module.
- HEX viewer: For advanced users, this module allows you to view any file content in HEX mode, providing a detailed look at file structures.
- PE files: Extract and view content from portable executable files like EXE, DLL, DPL, and more.
Seven of the ten viewer modules are accessible directly from the main interface, while the last three modules are invoked when a matching file type is detected. Using the viewer module allows you to leverage its specific capabilities when you know exactly what type of files you are about to open.
– Sponsored Links –
Recently Opened Files
From each viewer module and the File Analysis Report window, the “Most Recently Opened Files” feature in the Universal File Analyzer captures a convenient list of up to five of your most recently accessed files. With the ability to display up to five recently opened files, the list remains concise and easy to navigate, allowing you to quickly identify and revisit your important documents without the need to remember their specific locations.
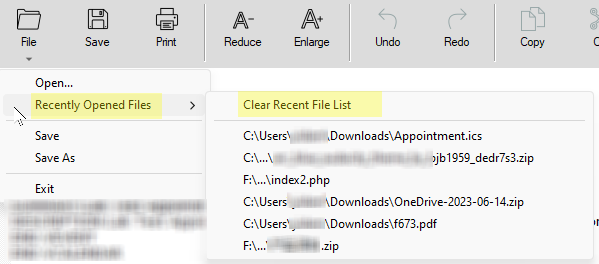
Click the “Clear Recent File List” menu item to erase the history of your recently accessed files. This action ensures that sensitive file information is no longer visible
Learn more about Universal File Analyzer
Maximize your experience with Universal File Analyzer by exploring the following topics.
Please note: help instructions for the Viewer Modules are illustrated using Universal File Viewer, which shares the same file viewer technologies as UFA.
– Sponsored Links –
– Sponsored Links –
– Sponsored Links –


